7 Life-Saving Steps to Handle Cardiac Arrest
7 Life-Saving Steps to Handle Cardiac Arrest
Learn everything you need to know about first aid for cardiac arrest in this comprehensive guide. Discover life-saving techniques, symptoms, and preventive measures to tackle cardiac emergencies effectively.

Introduction:
Cardiac arrest is a life-threatening emergency that requires immediate intervention. Knowing how to respond effectively can significantly increase the chances of survival. In this guide, we'll explore seven critical steps to handle cardiac arrest emergencies with confidence.
Understanding Cardiac Arrest:
Cardiac arrest occurs when the heart suddenly stops beating, leading to the cessation of blood flow to vital organs. This medical emergency requires prompt action to restore the heart's normal rhythm.
Understanding cardiac arrest is paramount for anyone looking to respond effectively in emergency situations. Cardiac arrest occurs when the heart suddenly stops beating, leading to the cessation of blood flow to vital organs throughout the body. This medical emergency is often confused with a heart attack, but they are distinct conditions with different causes and symptoms. In cardiac arrest, the heart's electrical system malfunctions, causing it to stop pumping blood. This can result from various factors, including underlying heart conditions, electrolyte imbalances, drug overdoses, or trauma.
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of cardiac arrest is crucial for prompt intervention. Symptoms may include sudden loss of consciousness, absence of pulse, and cessation of breathing. Prompt recognition enables bystanders to initiate life-saving interventions such as CPR (cardiopulmonary resuscitation) and the use of an AED (automated external defibrillator). Understanding the underlying mechanisms of cardiac arrest empowers individuals to respond swiftly and confidently, potentially saving lives in critical situations.

Recognizing the Signs and Symptoms:
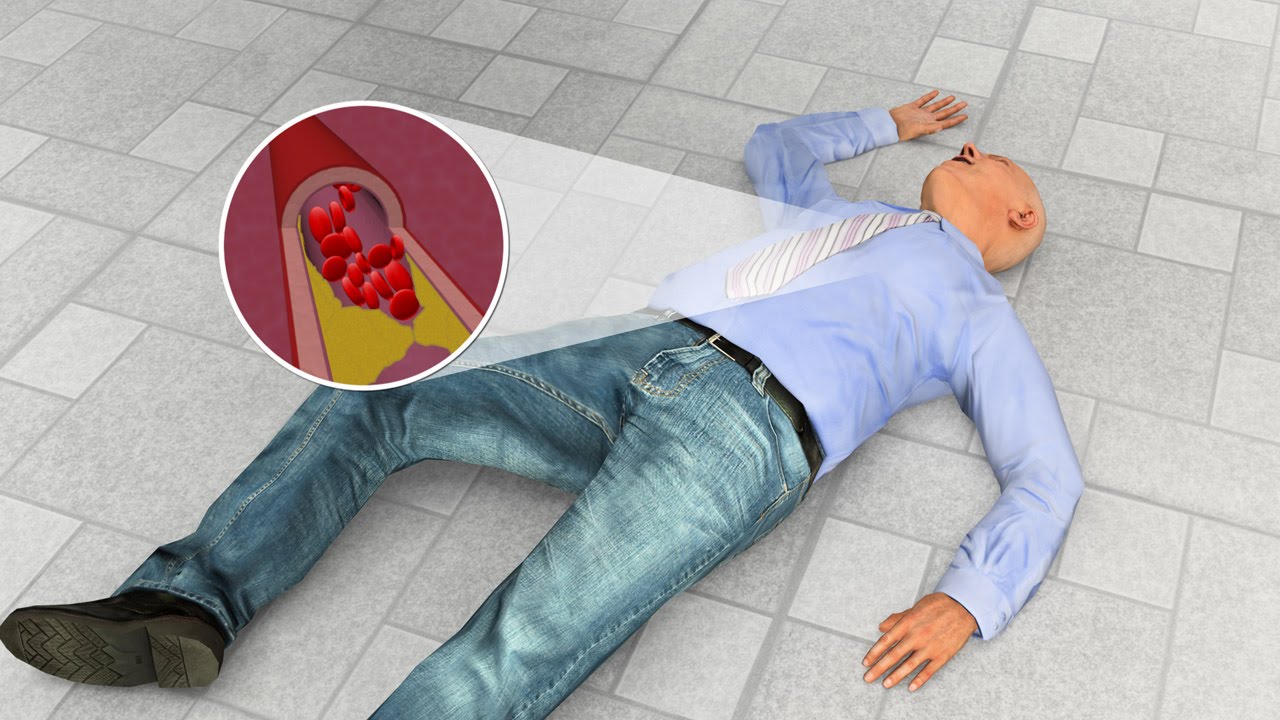
Identifying the signs of cardiac arrest is crucial for prompt intervention. Symptoms may include sudden loss of consciousness, absence of pulse, and cessation of breathing. Prompt recognition can facilitate timely assistance.
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of cardiac arrest is vital for timely intervention and potentially saving lives. Cardiac arrest often occurs suddenly and without warning, making it essential to be aware of its common indicators. One of the primary signs is the sudden loss of consciousness, where an individual may collapse unexpectedly. Additionally, there is usually the absence of a pulse, indicating that the heart has stopped pumping blood effectively. Observing the person's breathing is also critical; in many cases of cardiac arrest, breathing ceases or becomes irregular.
Other symptoms that may accompany cardiac arrest include gasping for breath, a pale or blueish skin tone, and a lack of responsiveness. It's crucial to note that these signs can vary from person to person, and not everyone will exhibit the same symptoms. Therefore, it's essential to remain vigilant and act quickly if you suspect someone is experiencing cardiac arrest. By promptly recognizing these signs and symptoms, bystanders can initiate CPR, use an AED if available, and call for emergency medical assistance, significantly improving the chances of survival for the individual in distress.
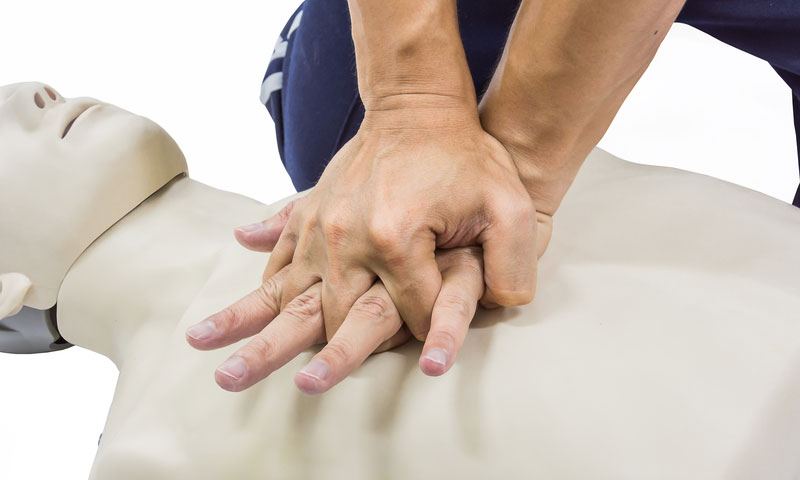
Performing CPR (Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation):
CPR is a vital intervention for cardiac arrest victims. It involves chest compressions and rescue breaths to maintain blood circulation and oxygenation until advanced medical help arrives. Proper CPR technique is essential for maximizing survival chances.
Performing CPR (Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation) is a crucial skill that can be life-saving in the event of cardiac arrest. CPR is a technique designed to maintain blood circulation and provide oxygen to the brain and vital organs when the heart has stopped beating. It involves a combination of chest compressions and rescue breaths to mimic the heart's pumping action and deliver oxygen to the body's tissues.
To perform CPR effectively, begin by assessing the person's responsiveness. If they are unresponsive and not breathing normally, immediately call for emergency medical assistance. Then, place the person on their back on a firm surface and kneel beside them. Position your hands in the center of their chest, interlocking your fingers, and begin chest compressions. Push down firmly and rapidly, allowing the chest to rise fully between compressions. Aim for a rate of around 100 to 120 compressions per minute.
After performing a series of chest compressions, deliver rescue breaths by tilting the person's head back slightly, lifting their chin, and pinching their nose closed. Place your mouth over theirs and give two breaths, each lasting about one second, while watching for the chest to rise. Continue cycles of chest compressions and rescue breaths in a ratio of 30 compressions to 2 breaths until help arrives or the person shows signs of recovery.
It's important to remember that any attempt at CPR, even if performed imperfectly, can significantly increase the chances of survival for someone experiencing cardiac arrest. While CPR should ideally be performed by trained individuals, even bystanders with minimal training can make a difference in saving a life. Regular CPR training and certification are recommended to ensure readiness and proficiency in performing this life-saving technique.
Using an Automated External Defibrillator (AED):
AEDs are portable devices that deliver electric shocks to restore the heart's normal rhythm. These devices are user-friendly and can be used by bystanders with minimal training. Early defibrillation is crucial for improving survival rates.
Using an Automated External Defibrillator (AED) is a critical step in responding to cardiac arrest emergencies. An AED is a portable device that delivers an electric shock to the heart to restore its normal rhythm. These devices are designed to be user-friendly and can be used by bystanders with minimal training.
When an AED is available, it should be retrieved and turned on promptly. The device typically provides clear audio and visual instructions to guide users through the process. Before attaching the AED pads to the person's chest, it's important to ensure that the area is dry and free from any obstructions such as jewelry or clothing.
Once the pads are applied, the AED will analyze the person's heart rhythm and determine if a shock is needed. If the device advises delivering a shock, bystanders should ensure that no one is touching the person and press the shock button as instructed. After the shock is delivered, CPR should be resumed immediately, following the AED's prompts.
Using an AED alongside CPR can significantly improve the chances of survival for someone experiencing cardiac arrest. These devices are designed to be safe and effective, even for individuals without medical training. By having AEDs available in public places and ensuring that people are trained to use them, communities can increase the likelihood of successful outcomes in cardiac emergencies.
Calling for Emergency Medical Assistance:
Prompt activation of emergency medical services (EMS) is essential for cardiac arrest management. Dialing the emergency number and providing accurate information about the situation can expedite the arrival of trained medical personnel.
Calling for emergency medical assistance is a crucial step in responding to a cardiac arrest emergency. Prompt activation of emergency services ensures that trained medical personnel can arrive quickly and provide advanced care to the individual in distress.
When you witness someone experiencing cardiac arrest, immediately dial the emergency number (such as 911 or local emergency services) and provide the dispatcher with essential information about the situation. Be prepared to provide details such as the location of the emergency, the individual's condition, and any actions that have been taken, such as CPR or the use of an AED.
It's essential to stay on the line with the dispatcher and follow their instructions carefully. They may provide guidance on how to perform CPR effectively or use an AED if one is available. Providing accurate information and remaining calm can help expedite the arrival of emergency responders and ensure that the individual receives timely and appropriate care.
Remember that every second counts in a cardiac arrest emergency, and early intervention can significantly impact the person's chances of survival. By calling for emergency medical assistance promptly, you are playing a crucial role in helping to save a life.
Administering Medications:
In some cases, administering certain medications may be necessary to support cardiac function and stabilize the patient. However, medication administration should be performed by trained healthcare professionals.
Administering medications is a critical aspect of managing cardiac arrest, but it's important to note that medication administration should typically be performed by trained healthcare professionals. In the context of cardiac arrest, certain medications may be administered to support cardiac function and stabilize the patient's condition.
One of the primary medications used in cardiac arrest management is epinephrine, also known as adrenaline. Epinephrine works to stimulate the heart and increase blood flow to vital organs, helping to improve the chances of restoring a normal heart rhythm.
Other medications that may be administered during cardiac arrest include antiarrhythmic drugs such as amiodarone, which help to control abnormal heart rhythms, and sodium bicarbonate, which can be used to correct acidosis in the blood.
The decision to administer medications during cardiac arrest is typically based on the patient's specific condition and medical history, as well as established protocols and guidelines. It's essential that medications are administered at the appropriate dosages and via the correct route, which may include intravenous or intraosseous administration.
While administering medications is an important aspect of cardiac arrest management, it's crucial to recognize that CPR and defibrillation remain the cornerstone of treatment. Medications are typically used as adjuncts to these interventions and should be administered in conjunction with ongoing resuscitation efforts.
Overall, medication administration in the context of cardiac arrest underscores the importance of a coordinated and multidisciplinary approach to patient care, with healthcare professionals working together to optimize outcomes for individuals experiencing this life-threatening emergency.
Ensuring Adequate Post-Resuscitation Care:
After successful resuscitation, ongoing medical care is vital for optimizing patient outcomes. Monitoring vital signs, managing complications, and addressing underlying causes are crucial aspects of post-resuscitation care.
Ensuring adequate post-resuscitation care is essential for optimizing patient outcomes following a cardiac arrest. While successful resuscitation is a crucial first step, ongoing medical attention and monitoring are necessary to support the patient's recovery and prevent complications.
After resuscitation, healthcare providers focus on stabilizing the patient's condition and addressing any underlying causes of the cardiac arrest. This may involve monitoring vital signs such as heart rate, blood pressure, and oxygen saturation, as well as assessing neurological function and overall organ perfusion.
In some cases, patients may require additional interventions such as mechanical ventilation to support breathing or medications to manage complications such as arrhythmias or hypotension. Close monitoring in an intensive care setting allows healthcare providers to promptly identify and address any changes in the patient's condition.
Beyond immediate medical interventions, post-resuscitation care also encompasses addressing the emotional and psychological needs of the patient and their loved ones. Surviving a cardiac arrest can be a traumatic experience, and patients may benefit from counseling and support services to help them cope with the aftermath of the event.
Rehabilitation and cardiac rehabilitation programs play a vital role in the long-term recovery process, helping patients regain strength, mobility, and confidence after a cardiac event. These programs often include exercise training, education on heart-healthy lifestyle habits, and emotional support to promote overall well-being.
By ensuring comprehensive post-resuscitation care, healthcare providers can help maximize the chances of a full recovery and improve the quality of life for patients who have experienced cardiac arrest. This holistic approach emphasizes the importance of ongoing support and monitoring to support patients on their journey to recovery.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions):
What are the common causes of cardiac arrest?
Cardiac arrest can be caused by various factors, including underlying heart conditions, electrolyte imbalances, drug overdoses, and trauma.
How can bystanders help in a cardiac arrest emergency?
Bystanders can play a crucial role by performing CPR, using an AED if available, and promptly calling for emergency medical assistance.
Is it necessary to perform CPR even if an AED is available?
Yes, CPR should be initiated immediately, even if an AED is available. CPR helps maintain blood circulation until the AED is ready for use.
What is the survival rate for cardiac arrest outside the hospital setting?
Survival rates for out-of-hospital cardiac arrest vary depending on various factors, including the bystander response, promptness of CPR and defibrillation, and underlying health conditions of the patient.
Can cardiac arrest be prevented?
While cardiac arrest cannot always be prevented, adopting a healthy lifestyle, managing underlying health conditions, and undergoing regular medical check-ups can reduce the risk.
What should I do if I witness someone experiencing cardiac arrest?
If you witness someone experiencing cardiac arrest, immediately call for emergency medical assistance, start CPR, and use an AED if available. Every second counts in saving a life.
How can I learn CPR and AED skills?
Many organizations offer CPR and AED training courses, including healthcare providers, community centers, and online platforms. Enrolling in a certified training program can equip you with life-saving skills.
Conclusion:
Being prepared to handle cardiac arrest emergencies can make a life-saving difference. By familiarizing yourself with the essential steps outlined in this guide and staying calm under pressure, you can contribute to saving lives in critical situations.
First aid kits convenient managed rental service ensures whs compliance with lifetime refills. Hs and ts is the name for a mnemonic used to aid in remembering the possible treatable or reversible causes of cardiac arrest.
First aid is the assistance given to any person suffering a serious illness or injury with care provided to preserve life prevent the condition from worsening.
First aid is the immediate assistance provided to any individual experiencing a serious illness or injury. The primary goal of first aid is to preserve life and prevent the condition from worsening until professional medical help arrives. This can involve a range of interventions, including assessing the person's condition, providing basic medical care, and initiating emergency procedures as needed.
First aid techniques may vary depending on the nature of the illness or injury. Common first aid measures include assessing the person's airway, breathing, and circulation, as well as controlling bleeding, immobilizing injured limbs, and providing support and reassurance to the individual.
First aid responders are trained to quickly assess the situation, prioritize care based on the severity of the condition, and take appropriate action to stabilize the person's condition until further medical attention can be obtained. In some cases, first aid may involve administering CPR (cardiopulmonary resuscitation), using an AED (automated external defibrillator), or managing medical emergencies such as choking, allergic reactions, or cardiac arrest.
Effective first aid requires not only technical skills but also calmness, confidence, and compassion. By promptly administering first aid, individuals can significantly improve the chances of a positive outcome for those in need, potentially saving lives and minimizing the impact of injuries or illnesses.